SvelteKit is a framework for building web applications of all sizes, with great development experience and flexible file-based routing. The framework combines single-page apps' SEO and progressive enhancement benefits with the quick navigation of server-side rendered applications. One of the critical features of SvelteKit is its routing system.
Understanding SvelteKit Routing
SvelteKit is a frameworkbuilt on top of Svelte. In SvelteKit, routing follows a file-based system. This means that your pages' directory structure determines your application’s routes.
To understand the SvelteKit routing system better, first, create a SvelteKit project. To do this, run the following code in your terminal:
After running the code block above, you will answer a series of prompts to configure your application.
Next, install the necessary dependencies for your project. To do thiscdinto your project and run:

Open the project on the development server by running the following command in your terminal:
Now, your project will be up and running onhttp://localhost:5173/. When you open the application on your development server, you will have an interface similar to the image below.
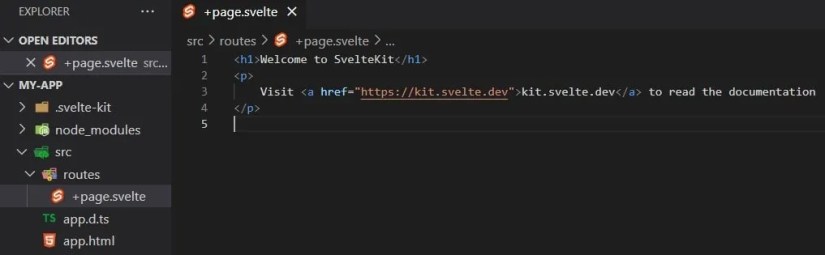
The project’s root route‘/’corresponds to a file named+page.svelte. You can find the+page.sveltefile following the file path;src/routesin your project.
To create different routes in SvelteKit, you can create folders in yoursrc/routesdirectory. Each folder will correspond to a different route. Generate a+page.sveltefile in each folder to define the content of that route.

The code above will live inside the+pagefile. You will create a svelte file inside theaboutfolder in thesrc/routesdirectory. This file will contain the content for the route. To view the route in your web browser, navigate tohttp://localhost:5173/about.
Navigating to the/aboutroute will display this interface on your screen:
Understanding Nested Routes
Nested routes are a way to structure the routing system in a web application. In a nested route structure, routes are placed within other routes, creating a hierarchical relationship between them. You can create nested routes in SvelteKit by placing folders with the+page.sveltefile inside other route folders under thesrc/routesdirectory.
For example:
In this example, you nest thepostroute within theblogroute. To nest thepostroute within theblogroute, create thepostfolder and its+page.sveltefile inside theblogroute folder.
To access the blog route in your application, open your web browser and navigate tohttp://localhost:5173/blog.

The post route will be available athttp://localhost:5173/blog/post.
Layouts and Error Routes
SvelteKit defines alayout for the application in a similar way to Next.js. Both frameworks use alayoutcomponent to define the structure of the application.
SvelteKit uses the+layout.svelteto define a layout for a group of pages. you may create a+layout.sveltefile in thesrc/routesdirectory to define a layout for all pages in your application or in a subdirectory to define a layout for a specific group of pages.
Here is an example of how to define a layout route for your entire application:
The example above provides a layout route. The file contains ah1element that displays the text"This is a SvelteKit application.“It also includes aslotelement. Theslotelement is a special element that defines the location where the application will render the content of your routes within the layout.It works the same way as Vue components.
In this case, your application will render the contents of your routes below theh1element.
To define an error page, create a file named+error.sveltein thesrc/routesdirectory. This page will display when an error occurs during rendering.
When you encounter an error, such as navigating to a non-existent route, your application will fall back to thiserrorroute instead.
The routehttp://localhost:5173/godoesn’t exist, so the application renders theerrorroute instead.
Navigating Between Pages
Finding the best way to navigate between the routes you create is crucial for a good experience. Traditionally, file-based routing in most technologies uses links to navigate between different pages. To navigate between pages in SvelteKit, you may use a simple HTML anchor tag.
For example, you may write this code in any route you want, but you should write it in thelayoutroute above theslottag:
Clicking on any anchor tag will navigate you to the corresponding route.
Dynamic Routing in SvelteKit
Dynamic routing allows you to progressively create routes the application generates based on data or parameters. It enables you to create flexible and dynamic web applications that handle different routes and display content according to specific data or parameters.
To create a dynamic route in SvelteKit, create a folder named[slug]and then a+page.sveltefile in the folder to define the route’s content. Note that you can name the folder whatever you like but ensure to always wrap the name in brackets [ ].
Here is an example of a dynamic route:
To access this route in your web browser, navigate to this linkhttp://localhost:5173/[slug], where[slug]can be any unique undefined route name you choose.
You can access your application’s[slug]parameter using the$page.paramsdata from$app/stores.
Here, you assign the$page.paramsobject to theparamvariable and render theparam.slugdata in your application.
The application retrieves theparam.slugdata from your link. For example, if you navigate tohttp://localhost:5173/fire, the content displayed on the application will be"This is the fire page.”
Now You Know the Basics of Routing in SvelteKit
Routing in SvelteKit is a powerful feature that allows you to structure your application in a way that makes sense. Understanding how to use this feature will enable you to create more efficient and user-friendly web applications. Whether creating a small personal project or a large-scale application, SvelteKit’s routing system has the tools you need to succeed.
Q: How Does Svelte Itself Handle Routing?
Sveltekit’s built-in routing support gives you less flexibility, but it also keeps things simple. If you’re using plain Svelte, you’ll need to usean external library like svelte-routing.
Q: How Do Other Frameworks Handle Routing?
Most frameworks support routing one way or another.Angular’s built-in routing supportis excellent, whileVue supports routing via its official vue-router package.
Q: How Popular Is Svelte?
Svelte is one ofthe most popular JavaScript frameworks. In fact, 2023’s Stack Overflow survey found that developers admire it more than any other.